Plant growth regulator
6-Benzylaminopurine (BAP) Application:
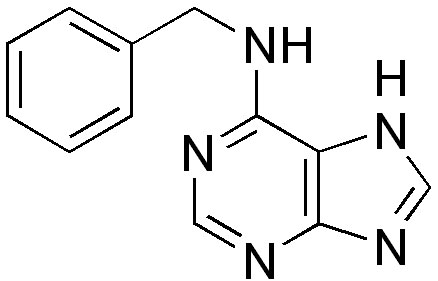
6-Benzylaminopurine, benzyl adenine or BAP is a first-generation synthetic cytokinin that elicits plant growth and development responses, setting blossoms and stimulating fruit richness by stimulating cell division. It is an inhibitor of respiratory kinase in plants, and increases post-harvest life of green vegetables. Influence of cytokinin as 6-benzylaminopurine (BAP) in combination with other methods on postharvest green color retention on broccoli heads and asparagus spears, showed positive results for quality retention. Treatment with 10 and 15 ppm BAP can be used to extend shelf life of fresh-cut broccoli florets and shredded cabbage during storage at 6±1°C at commercial level.
It can accelerate growth of cell. When used with gibberellins, fruit’s shape can be improved. 6-Benzylaminopurine stimulates the following effects: cell division; lateral bud emergence (apples, oranges); basal shoot formation (roses, orchids); flowering (cyclamen, cacti); fruit set (grapes, oranges, melons).
6-Benzylaminopurine (BAP) effects:
BAP effects:
- Cell division;
- Lateral bud emergency ( for example: apples, oranges);
- Basal shoot formation ( for example: roses, orchids);
- Flowering ( for example: cyclamen, cacti);
- Fruit setting ( for example: grapes, oranges, melons).
6-Benzylaminopurine (BAP) Recommended dosage:
Treatment with 10 and 15 ppm BAP can be used to extend shelf life of fresh-cut broccoli florets and shredded cabbage during storage at 6±1°C at commercial level.
GRADE & FORMULATION:
Technical: 98% TC
 |
 |
CAS Number: 1214-39-7
BAP plant hormone instructions
More information:
Formula: C12H11N5
Molar Mass: 225.26 g·mol−1
- Other names
Benzyl adenine; 6-Benzyladenine